Introduction to Business Analytics and its importance
If there is a list of job profile that requires a person to have a knowledge and expertise in a range of filed and also requires the art to put the knowledge gained from various disciplines to accomplish a single objective, then the job of Business Analyst will be high on top.
As the name suggests, business analysts are primarily responsible for business analytics and this leads to the next logical question – what is business analytics? Though the question seems simple and straight forward, there sometimes seems a great mystery surrounding this field. This article aims to address all the relevant aspects of Business Analytics that can eventually help people to understand the scope of business analytics.
The very term “Business Analytics” holds the key to decipher the true meaning of it. While business refers to any organized commercial activity, the true meaning of analytics can be a bit tough to pinpoint. Analytics (in terms of Business Analytics) can be understood as a study that concerns itself with the scientific interpretation of the data using a range of pre-existing fields of study such as Mathematics, Statistics, and Information Technology. All these studies are put to use to discover the hidden patterns, meaning, and predictive capabilities hidden inside the data by systematically examining it.
While it would be right to say that Business Analytics as a discipline is fairly new, it would be wrong to say that it didn’t exist at all previously. Analytics has been present in one form or the other since the advent of organized business. Earlier, business analytics was a very disorganized field where a number of simple tools, basic arithmetic, and mainly human intelligence, experience, and intuition were put to use to gain some insights from the limited amount of data that was generated from the business organizations.
The field got a business analytics syllabus when it got formalized primarily due to the revolution in the field of technology. The two biggest achievements of the 21st century have been the immense progress made in the computational capabilities and the internet of things that have allowed a huge amount of data to be generated at every second that covers all aspects of a Business.
These when combined lead to a force that can allow individuals especially at the leadership position to know not only about what has happened to the business so far but also to what is happening and what will happen in the near future and in some cases, in the distant future too. This prospect, as exciting as it sounds, is the reason that the role of Business Analytics has gained immense importance.
The importance of business analytics can be understood in the context of organizations that are at the various stages of their growth. For a very new company with very little historical data, the scope of business analytics is of providing insights through which the companies could innovate and lead to growth.
For example, by analyzing the data of the customer’s preference, E-commerce companies early on realized the importance of introducing the Cash one Delivery as the mode of payment which was unheard of in the west (which had been the traditional location for the E-commerce companies to operate). Such business insights allowed the early Indian E-commerce companies to expand in India which till a short while back had been considered as a very less electronic-payment friendly market and mainly ran on hard cash.
Business Analytics further provided insights to create different strategies for the urban and rural markets with urban households having more penetration of digital money thus incentivizing such mode of payment and slowly getting rid of cash on delivery. For a mid-size company, it is highly important to trace their steps and identify the fault lines much before they become big enough to correct.
Sales of a product after its initial success becoming stagnant can lead to the fall of such companies and identifying if the fault lies in marketing or after-sale services or some aspect of the product itself is something business analysts need to take care of.
A large business organization is perhaps the biggest employer of the business analysts as it has a huge amount of data lying around which can be described as a gold mine and requires talented miners to find value in it. Such companies need to discover ways to expand by analyzing markets and customers, understand the problems that might be facing a new project, and also recommend solutions for it.
If you’re considering a career as a business analyst in 2024, our tailor-made courses are just the right option for you to begin your learning journey!
Explore our Business Analytics 360 course and join us for experiential learning that will transform your career. Check out our upcoming batches or book a free demo with us. Also, check out our exclusive enrollment offers
A precise understanding of the role of business analytics can be understood by understanding the different types of Business Analytics that will be discussed ahead.
Components of Business Analytics
Like every other field, Business Analytics is also comprised of multiple components that one must know about before picking it up as their career path. Each of these components is equally important and serves some purpose in the larger picture of data-driven analytics. To understand the individual components of Business Analytics, an understanding of the overall business analytics process can be highly important.
The process of business analytics starts from realizing that there is some problem or there is a scope of improvement. This is where good business acumen is required whereby understanding the inner working of the business, one can help and guide in the area of interest.
The next step is often retracing the steps and checking if the process is going in the rights direction or not. This is where, business analysts much check that something that they are considering as a problem or scope of improvement actually exists or not.
Once all of this is cross-checked, then business analysts need to identify the relevant data required to do the job. This includes the identification of the data source, the type of data required, the amount of it, and the format in which it can become useful.
This is where Data Engineer also come in the scene as they are often responsible for creating the architecture to perform ETL operations that allow the Business Analysts to get hold of relevant data in a relatively short span of time.
Once the data is achieved, it is treated, cleaned, prepared, and finally is put to use. Here various methodologies are put to place that provides varied kind of information from the data. While some are simply factual in nature, some provide predictive information.
All these aspects of the analytical process form the different components that are namely-
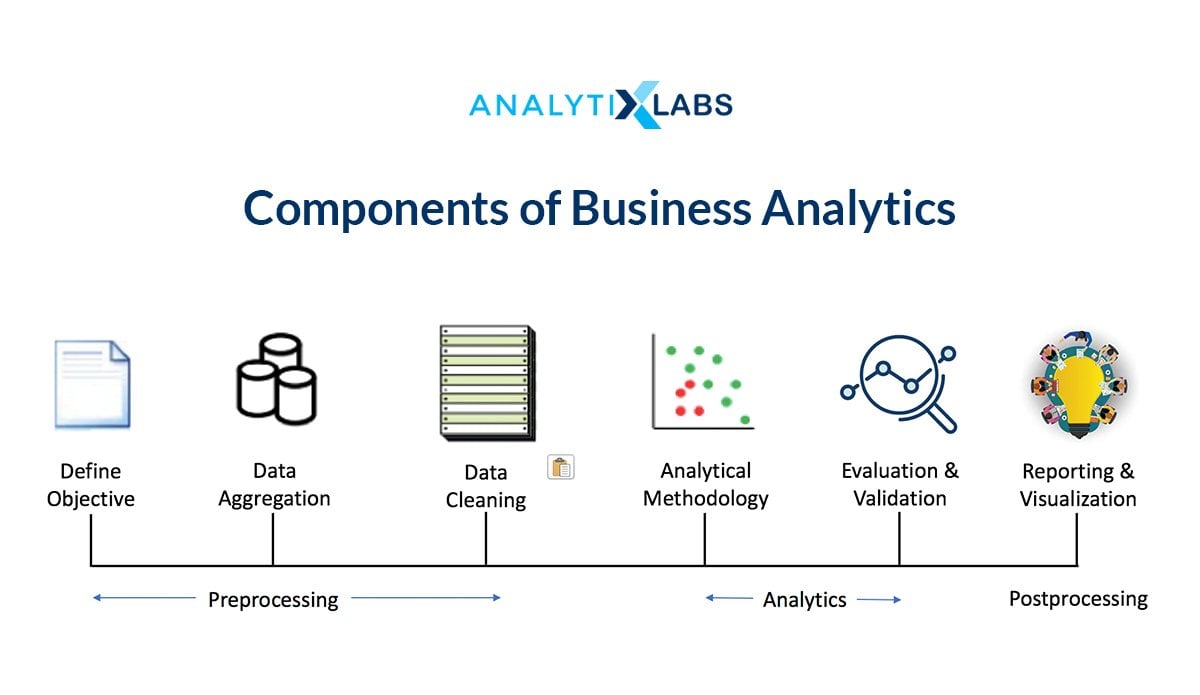
Define Objective
This is the foremost step. Without having a clear understanding of business goals, questions we need to answer, and problems we ought to solve, none of the following steps will deliver. This also helps us to translate business objectives into analytics objective and map data requirements.
Data Aggregation
The process of having a centralized location for the data, extracting and loading the relevant data by putting relevant filters, and creating subsets of data is the core aspect of Data Aggregation. This is where the data is transformed depending upon the business requirement. Also data pertaining from various sources are combined to have one large dataset. The format of the data is also sometimes changed at this step to make it compatible with the tool being used to achieve the objectives.
Data Cleaning
Data Cleaning is an extremely important component of business analytics because the data in its raw form sometimes is not directly usable. As the other components of Business Analytics use mathematics, statistics, and computer programming, the data must be compatible with these streams of study.
For example, for applying statistics, the data mustn’t have any extreme values (also known as outliers), while for mathematics, there should no blank cells or missing values (as matrix operations become difficult) while for programming, the concept of type casting plays a role where the data is made sure to be in the right format (i.e. correct class or data type).
Also, the concepts of multicollinearity and curse of dimensionality come in play as the business analyst has to make sure that there are no implicit or explicit duplicate columns. The importance of getting rid of the unnecessary columns can only be understood once a good grasp of statistics is there. Other aspects include the resampling of data (under-sampling, oversampling, hybrid-sampling) removal of duplicate rows, etc.
Analytical Methodology
Having a detailed understanding of the different type of analytics out there dominate this component as this is where the analysts have to identify the method with which they will go to achieve their end goal. If the end goal is to understand what is the present situation of the business then that requires a different set of methods while if there is a need to identify which has happened in the past or what can happen in the future, then a different technique is required. Here, having the know-how of various procedures, methods, and algorithms is important, and knowing what to use, when makes one business analyst stand apart from the other. Different types of Analytics methods and tools are explained in the latter section.
Evaluation and Validation
Once the results come out, the next task is to understand if the result stands true given a different situation or not. This is where is predictive models are used and their evaluation and validation are conducted whereas, for other methods, various simulation techniques are put to use to identify the most plausible outcome, thus providing provide a very reliable result. Here also, the business analyst needs to learn a range of techniques to identify the shortcoming in their method, work on it, improve it, and make their insights stable and valuable.
Reporting and Data Visualisation
Perhaps the most important and often overlooked component of the discipline is the aspect of communicating the results in an easy to understand way. This requires innovation and creativity and is the reason that this field is open to all and not only to mathematicians, statisticians, or computer programmers. To quickly make people understand the complex insights discovered over weeks or even months, reports or presentations are created that have simple tables, bullet points, etc. On top of all this, visualizing the data plays a major role here as it allows the people in the leadership positions to quickly view where the organization is coming from and perhaps where they are headed. Business Analytics ought to know the various ways of visualizing the data, the transformation required to be done on the data to make it possible, and finding innovative ways to string together different information in a smooth storytelling method.
Types of Business Analytics Methods
As mentioned earlier, there are multiple types of analytics that can be performed in the larger field of Business Analytics. All these types solve a particular kind of business problem which makes it important to know how these various types are different from each other and when they should be used.
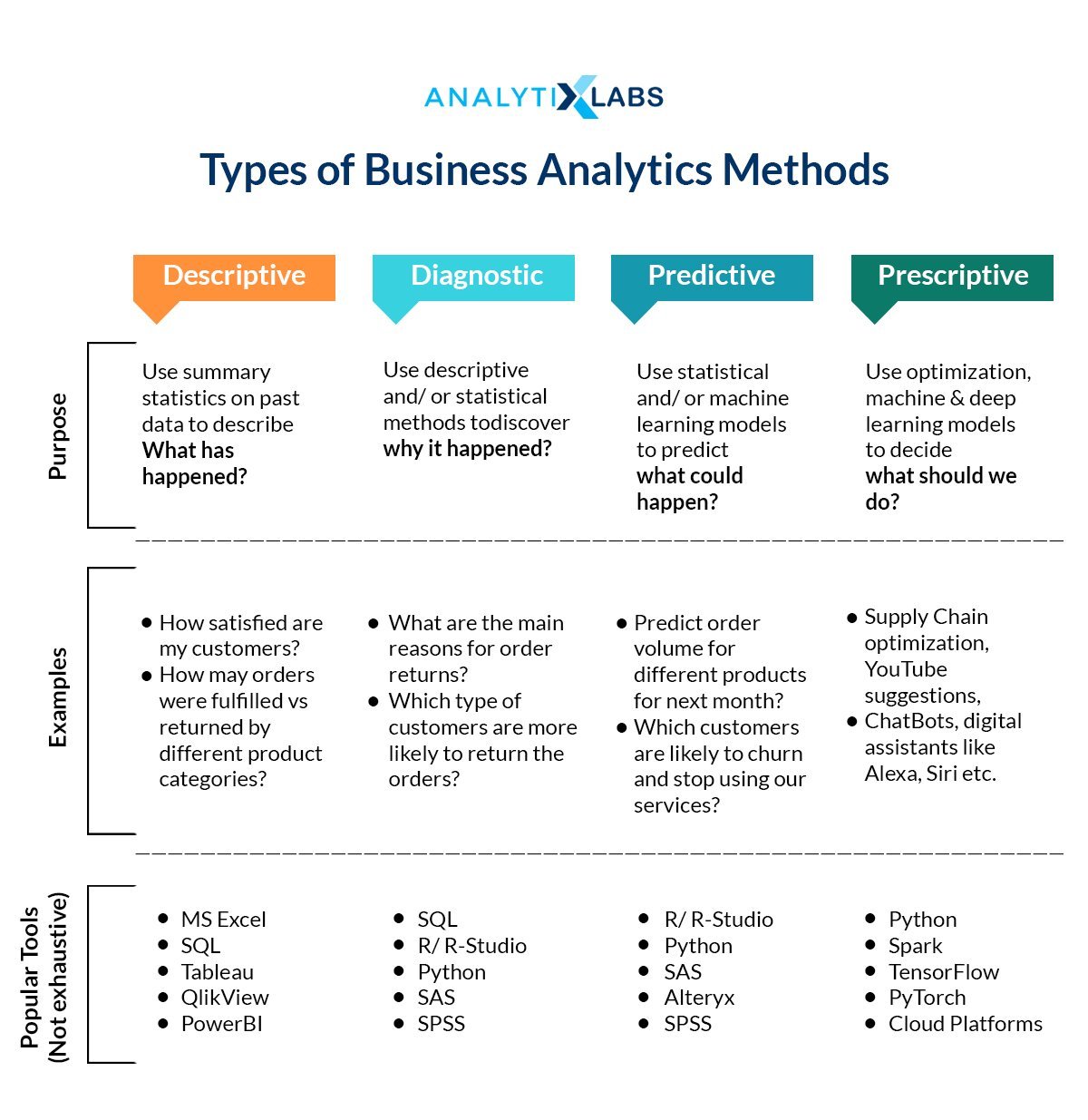
Descriptive Analytics
Perhaps the most basic and still the most important and widely used kind of analytics is descriptive analytics. This deals which uncovering the truth regarding business by analyzing the historical data. A number of factual information is revealed in this form of analytics. This is where, the grouping of data, use of descriptive statistics, and a number of visualization techniques come in handy. Here for example, by finding frequency, mean, median, mode, maximum, minimum values of a subject in different scenarios help in covering a lot of information. This allows the leadership to understand what has happened until now and gives a brief glimpse of what could happen next.
Diagnostic Analytics
This form of analytics deals with finding the reasons for whatever that has happened in the business so far. Methodologies such as Segmentation etc comes in handy where patterns are detected in the data to give a better insight into the scenario in which the company is present. For example, running analytics on the customer base of a company and identifying the different types of customers the company has been dealing with and targeting the specific kind of customers that might have been pulling back the companies’ growth.
Predictive Analytics
This is that branch of analytics that deals with the future. Here, again based on the historical data, a range of sophisticated statistical and machine learning methodologies are put to use to understand what can happen in the future given certain conditions or the pace at which the current scenario is moving. This is done by identifying patterns in the data, figuring out the important drivers and features, and finding its relation with the objective that we are trying to predict. Here terms such as Regression and Classification come in where Regression means predicting a numerical often continuous value while Classification means the prediction of a class or a category (or a limited amount of discreet numbers in some cases).
One must note that in none of these methods time is involved as when time gets involved then a particular kind of predictive analytics is performed known as forecasting. Forecasting refers to predicting a value over a fixed period of time where time also acts as a driver i.e. plays a role in deciding what the predicted value is going to be in the output.
Sometimes a very specific type of prediction is also performed such as Text Mining where texts are predicted to create products that can aid the business operation and can help in increasing the profits. In Predictive Analytics, advanced Machine Learning and Deep Learning algorithm are developed, and sometimes statistical models are also created.
Prescriptive Analytics
The most advanced form of analytics, here not only we try to predict but also try to find a course of action that is best suited to reach the objective. While predictable analytics provide us what will happen, prescriptive analytics provide us with the answer on how to avoid the prediction (in the case the predicted output is something not in the interests of the company). Different strategies are devised here and are put to use to check the different outcomes. This is where optimization and simulation methodologies are put to use and compared to the previously mentioned forms of analytics, this is a new and developing form of analytics. Advanced Machine & Deep Learning methodologies are often used in this type of analytics that allows us to create different scenarios and find the best course of action.
You may also like read: Types of Business Analytics – Types of Analytics With Examples
Important Business Analytics Tools
What is business analytics can also be answered by understanding the tools used in this field. As the discipline of business analytics is of a unique kind as it covers various types of analytics and this is the reason that there is a range of business analytics tools to accomplish the objectives.
As business analysts grapple with a number of problems that range from sourcing data to create predictive models, tools that specialize in different fields are put to use and a good business analyst must know how to use all of them in harmony. Some of the common Business Analytics related tools include:
SQL
It is among the most important tool as SQL queries allow the user to easily filter out and create subsets of an otherwise large dataset. By having the relevant amount of data, the analyst can quickly start working on the cleaning of the data and then creating models out of it. SQL sometimes is used with other tools such as OmniSci or Zeppelin by apache where PostgreSQL is used.
Tableau/ QlikView/ PowerBI
The most important tool for report generation through the means of visualization. Tableau allows the user to quickly create interesting, complex, and detailed graphs that can magnify the impact of a report. The good aspect of this tool is that it is easy to use and requires less data preparation in order to get the desired output.
Birt
Another useful report based tool allows us to create graphs and dashboards, however, it is relatively complex than tableau as the user needs to have a decent knowledge of Java to make the most out of it.
Python
One of the most advanced tools, python allows the user to perform multiple things. Python can be used to perform basic steps such as data cleaning to a complex aspect of analytics that includes the development of various kinds of models. The development of highly complex machine learning and deep learning model is particularly effective through this tool. Python also allows us to create reports and has libraries for visualization but it is up to the user to use them or use dedicated visualization tools.
R
This statistical tool created “by the statisticians for the statisticians”, allows a business analyst to perform all the descriptive and inferential statistics along with the development of statistical models. If compared to python it has a bit of a steep learning curve but this eventually pays off as it has a large community of users and is respected in the world of corporate as well as academia.
MS Excel
One of the most basic yet widely used and effective tool. The importance of MS Excel in the field of Business Analytics can be understood from realizing the difference between a sword and a needle. While for performing the complex operation of data extraction, model development, and report generation, there are several heavyweight tools. MS Excel on the other hand sometimes is used at the very end or sometimes in the very beginning to provide an easy, user interactive experience to gain quick insights regarding the data or the final output and this is the reason that still many times the final output is in the form of an Excel.
You may also like to read: Top 10 Data Analytics Tools For Everyone
Business Analytics Certifications Courses
In order to become a Business Analyst, firstly one needs to know what Business Analytics is all about. The next thing, of course, it to know the way through which once can land up a job as a Business Analyst. The question of How to becomes a Business Analyst is multifaceted as it has mainly two sides to it. The first being what one needs to have within and the other being what one needs to do and this is what is addressed below.
Basic Skills Needed to pursue a Business Analyst career
One can learn business analytics skills by going through a professional course on it but even before that there are certain pre-requisites that one must comply with before getting on with a course. Following are some of the pre-requisites

Understanding the nature of the job
One must understand the work of a Business Analyst. This article so far has given enough insights to give an idea as to what a Business Analyst work-life looks it and if that intrigues you then only the job of Business Analyst is the right choice.
Communication Skills
After all the technicalities of statistics and mathematics, the business analysts at the end need to communicate their insights with the leadership and often have to explain their process and provide suggestions, all of which require good communication skills. As the role of Business Analyst is not individual-based and several business analysts work on the same project together, keeping everyone on the same page regarding the process is highly important, and this is also where verbal as well as written skills are required to succeed.
Overall Aptitude and Creativity
Business Analytics cannot be performed by using ready-made tools and procedures and a good amount of out of the box thinking is required. Thus, a good business analyst must have all the theoretical knowledge of the methods and tools but also need to know to put them to use in a creative manner to find out insights that others might have missed.
Visualization and Reporting Skills
The art of finding meaningful insights from a large amount of often unsorted data is one thing, but to present all the insights in a coherent manner that can be understood by a large audience that may not have an understanding of statistics, etc is a whole different ball game. This is where having a sense of using the right type of visualization techniques to represent a particular insight is highly important.
Business Acumen
As mentioned during the process of business analytics, one of the foremost steps is to understand where the problem lies and in what direction to look at, and for this a good amount of business acumen is required. This is the reason that in several MBA courses, there are subjects on Business Analytics and their tools and for those who are not MBA, one must gain a decent amount of business knowledge to succeed in this field.
Basic Arithmetic Knowledge
Having basic arithmetic and statistical skills are highly important. As will be discussed later, the various course will hone the skills of the candidate in these fields but still having basic statistical and arithmetic information regarding average, frequency, median, aggregation, etc is something that one must already have.
Basic IT Knowledge and Skills
Again, the business analytics course allows the candidates to know several tools that require programming skills but having a basic computer and programming skills still is a must. For example, an aspirant must know how to use a computer and handle basic applications related to MS office and know the basics of programming such as what are loops, conditions, reusability of codes, etc.
Patience
The patience required to dedicate oneself to this field is highly important. It takes time to master the various skills of mathematics, statistics, programming, reporting, etc and it further takes time to get the knowledge about various domains and gain experience to be able to see the bigger picture that allows the user to sought through a large amount of information.
Also, read about: Prequisites of Business Analytics
Characteristics of a Good Business Analytics Certification Course
Once the pre-requisites are done, an aspirant must find ways to learn all the advanced skills to become a Business Analyst, and here Business Analytics courses can help. While there are a number of course out there that certify a person of having Business Analytics related knowledge, one must pick a course that covers the following-

Theoretical Aspects
A good course must cover all the theoretical aspects regarding the whole process of analytics. This should be further continued with an in-depth theoretical discussion on the statistical modeling techniques and mathematical algorithms. All of this will allow the learners to know of the advantages, and disadvantages of different methods and will further make them able to comprehend the inner workings of these methods/algorithms in a better manner.
Tools Covered
Tools are as important as the theoretical knowledge and a good business analytics certification makes sure that all the required tools are covered and the learners are exposed to a good amount of hands-on experience. Typical tools that a certificate must cover are Excel, Tableau, SQL, and R or Python as all of them handle one or the other aspect of Business Analytics.
Business Knowledge
The knowledge of the business cannot be gained overnight and a good course must at least provide case studies belonging to various business domains to inculcate the business intuition in the minds of the candidates. Courses having a good amount of Case Studies and Assignments belonging to different business sectors allow the learners to explore that business, find the common problems marring those industries, and gain the expertise in solving them.
Online and Classroom Platforms
While most of the courses are online, it is better if the course provides classroom lectures also as this allows for an additional, more personal experience of learning. Having classroom training allows the learners to directly get in touch with the trainers that help in getting a good amount of knowledge and confidence.
Job Assistance
The final aim of learning all of this is to finally land up a job as a Business Analyst. A good business analytical program must help in job assistance as that fulfills the end goal of a candidate. Also, the job should be in the concerned company providing the compensation typical in the field of Business Analytics. The Business Analytics Salary range from a typical average of 10 – 12 lakhs per annum with people having advanced knowledge often making more than 14 lakhs per annum.
Platforms for Business Analytics Courses
There are several platforms through which one can apply and go through the Business Analytics courses. Some of these platforms are purely e-Learning and offer recorded videos such as the courses on Coursera, Udemy, and edX.
There are academic institutions also that provide online courses such as Columbia University while for classroom experience, there are very limited institutions in India that offer courses in the field of Business Analytics.
AnalytixLabs provides both Classroom bootcamps as well as Online course in Business Analytics and covers all the above-mentioned tools and theoretical aspects and engages with the students through a number of case studies belonging to different domains that provide a hands-on experience to the learners.
The field of Business Analytics is complex, fascinating, and also demanding. While this field is open to all, people who have the ability to look at the bigger picture, are inquisitive and love problem solving must think of it as their career path. The demand for Business Analysts is at an all-time high and will remain so in the future. As it takes a dedicated journey to become a Business Analyst, one must start learning the required skills at the earliest.
You may also like to read:
1. Why is Business Analytics a good career option?
2. Evolution of Business Analytics | Business Analytics Future
3. Best Ways to Learn Business Analytics | Courses & Free Resources








