Business Analytics has become an integral part of business operations and performance management. Businesses and corporations who wish to gain a competitive edge in the market during modern times must employ the services of skilled business analysts to do so. Without utilizing data effectively and without a dedicated analytics team, companies will not be able to sustain themselves in this world where the competition employs various analytical tools and techniques to facilitate peak performance. It’s not just about performance, as business analytics can help companies increase revenue by cutting costs and decreasing waste.
Companies can now judge their markets better, understand how their products perform against substitute products from other companies and analyze how consumers react to their services or products. With the valuable information and insights gained from data sourced or generated, organizations can make better data-driven decisions that can help them become successful. Business analytics is also about sustainability and the efficient use of resources. Without skilled business analysts, companies will not effectively conduct their businesses anymore. From finances and marketing to performance or operations analytics, business analytics is being used everywhere to optimize a company’s operational (business) affairs. Business analytics has existed for a long time, even without the advanced tools and techniques we have at our disposal now. For instance, merchants used to rely on handwritten annotations to contemplate their business’s annual performance. Smart business people used to study products based on surveys and reviews and understand what made consumers buy products and recurrently use (buy) them. However, all of this was done manually and took uptime. This completely changed when tools for advanced business analytics were slowly introduced into our society. Along these came the later generations of business analysts that would change the world forever. The evolution of business analytics was welcomed with open arms by corporations around the world.
Explore our Business Analytics 360 course and join us for experiential learning that will transform your career. Check out our upcoming batches or book a free demo with us. Also, check out our exclusive enrollment offers
This article will cover the evolution of Business Analytics throughout the years. We will also discuss how the future looks like in Business Analytics.
1. Evolution of Business Analytics
In recent times, business analytics has evolved into a much more advanced set of tools and techniques assisted by automation and big data. Initially, business analytics was limited to a few corporate applications used by only the major MNCs. The first adoption of computing for business was noticed in the use of report-building, presentations and data entry using applications such as Microsoft Excel. Later on, more advanced applications that involved multi-dimensional data processing and data analytics were seen using add-ons such as PowerPivot in Excel. This was still a long way from BI or business intelligence, which the highly accredited firm, Gartner.
Once the concept of BI was introduced into the market, corporations around the globe wanted their hands on it. BI used various digital instruments, technologies, and metrics to evaluate business performance and helped companies get valuable insights. This facilitated more informed decision-making and ensured that all the important organizations during that time adopted software such as Tableau, SAS, or Microsoft Power BI to support their business activities and operations. With BI, concepts such as ‘web questions,’ collaboration, data security, and sourcing data from databases and distributed file systems came into mainstream use as well. By now, business analytics was not just used by large MNCs and conglomerates but also medium-level and much smaller enterprises as well. This introduced the world to an era where analytics helped create research models, design models, and simulators that further helped companies use data to forecast and predict future outcomes more accurately than ever.
2. Business Analytics Historical Facts
Analytics and visualizations have been used throughout history without the support of computers and software. This was done by manually plotting graphs using statistical methods and manually recording data. This was quite different from the business analytics that we recognize and know about. The more modern version of business analytics was only used much later in the 20th century to identify trends during the Second World War. This process of identifying trends helped code-breakers use data from encrypted messages such as destination (recipients of the messages), origin, and the time and date of these messages to find out what information these contained. This is a more modern use of analytics to predict information. However, we have also seen business analytics being used a bit earlier in history. Sir Henry Furnese, a well-documented banker, had been extensively using data during the 1860s to stay ahead of his competition.
Here are some more historical facts about business analytics:
- During the early 1900s, Henry Ford, inspired by Frederick Taylor’s scientific management system, hired him in order to measure the performance of the assembly line of his famous Ford Model T. This led to a series of events that had transformed the manufacturing industry and production lines across the world. This also helped Henry Ford make his assembly line as efficient as possible.
- In 1956, IBM introduced the first hard disk drive that allowed users to store data that can be used for business or corporate purposes.
- During the 1970s, Bill Inmon started discussing the concept of a data warehouse to solve the problem of storing vast amounts of data for business intelligence.
- During the 1980s, the first business data warehouse was developed by IBM researchers Barry Devlin and Paul Murphy.
- In this period between the 1990s and early 2000s, various solutions and software were introduced, such as business intelligence tools by companies like SAP, Microsoft, SAS and IBM alongside relational databases.
- After the early 2000s, common people started using data more proactively for personal purposes. This also led to more corporate use of data through employees extensively using organisational data. More tools were also introduced during this time with which individuals can use business intelligence tools without extensive training. Eventually, Google Analytics was introduced that allowed website owners to analyse statistics about their website, such as trends in website visits.
- After 2010, business intelligence and analytics truly took off, being adopted worldwide by companies and businesses around the world. This also pushed us to an era of cloud computing and extensive use of Artificial Intelligence or automation.
3. Recent Evolution in Business Analytics
The recent evolution that business analytics has experienced can be fundamentally traced back to the introduction of automation in analytics and the concept of big data. The advent of big data meant that analytics along with various data sources should become more scalable and more powerful. This helped in introducing more advanced tools and systems that are compatible with large volumes of data. The emergence of cloud technologies also meant that data did not need to be on-site. There was also a huge demand for automating analytical tools by this time due to the massive amount of data that needed to be worked upon. All of this motivated companies to upgrade their existing software into more capable applications that can process massive datasets rapidly and from multiple sources such as from the cloud and distributed file systems rather than just the traditional RDBMS. Business analysts were also now armed with predictive and forecasting abilities that were now more accurate than ever with the help of modern business analytics. This is where businesses truly understood the importance of data analytics in business. All this technology had already existed, but the industry’s growing requirement encouraged businesses of all sizes to start incorporating data analytics into daily operations.
There have been four main spheres where business analytics has evolved greatly, these are:
- Artificial Intelligence and Automated Analytics
- Predictive Analytics
- Real-time Analytics
- Big Data

4. Why Business Analytics Is Essential To Build A Competitive Business?
Here are some reasons why Business Intelligence and analytics are essential for a successful business:
- Business analytics is very helpful in reducing risk in business operations.
- It increases revenue and helps companies churn out more profit.
- Analytics allow companies to make better and more informed business decisions that are data-driven.
- It helps increase the operational efficiency of projects or processes.
- It also helps in effectively using resources such as human assets.
- It helps in reducing wastage and in cutting operational costs.
- Business analytics directly allows companies to stay ahead of their competition and outperform them.
- Analytics optimises processes and helps in business process automation.
- It also allows companies to replicate successful results and understand how the success was achieved.
- It helps in forecasting and prediction of outcomes.
- Business analysts help monitor performance and evaluate operations through identifiable metrics or Key Performance Indicators(KPI).
- It helps in the identification of anomalies and factors that affect market and customer behaviour.
- Real-time business analytics helps in taking rapid data-centric decisions.
- It helps in improving the sustainability of businesses and projects in the long run.
5. Big Data – Overview
Data is the most important aspect of business analytics. The Meaning of ‘big data is, fundamentally, data that is too complex, and more importantly, too massive to be processed by traditional methods or software. Modern business analytics is highly focused on mining, analyzing, and extracting insights from large datasets. This is why big data is a huge deal in this day and age. Companies collect massive chunks of data on a daily basis as they keep operating, and this data consists of multiple complex pieces of information associated with customers, products, performance, finance, etc., that must be maintained properly and then effectively used for future operations. For instance, businesses can use past data collected over many years to predict customer behavior, such as buying patterns. Or, banks can use customers’ credit history when deciding upon eligibility. Histories of other customers can also be studied to predict the likelihood of certain events, such as buying substitute products.
Big data is a treasured part of business analytics, and analysts have started getting comfortable working with big data in organizations of all sizes. Big data has also directly encouraged the use of Machine Learning (ML) when working with massive datasets. ML allows data to be extracted without errors, structured and utilized much more effectively.
6. Advantages of Big Data For Business Analytics
Here are some advantages of using Big Data for Business Analytics:
- More Informed Decision Making:
Big data allows companies to work with a huge amount of user or customer data that allows them to make better decisions. A lot of past or historical data also helps companies predict more accurately.
- Faster Decision Making:
Using machine learning, big data can predict and identify patterns rapidly. This speeds up decision-making and allows businesses to use a lot of data very fast. The compiled data can also be processed alongside fresh incoming data, which has helped companies make informed decisions in real-time.
- Cost Reduction:
Generating and collecting your own data is the most cost-effective method, as sourcing data from third parties is much more expensive. Also, saving past data enables you to generate only the relevant data and not waste time on generating the same leads or information again. Also, big data, in general, helps businesses cut costs. Thus, the importance of data analytics in business is truly seen when companies increase their revenue with the help of big data.
- Providing Better Service to Customers:
With the help of big data, companies can understand customers’ buying behavior and can then effectively provide the after-sales services or complementary services that they might require. With the help of an enormous amount of data such as posts, comments, and messages on social media, companies can even figure out customer sentiments and how satisfied these customers are with the company’s products or services.
- Finding New Opportunities:
Businesses can discover new opportunities with such huge volumes of data. With the help of this data, businesses can come up with major solutions to problems or come up with fresh concepts and product ideas. They might also be able to figure out how to improve sales or reach out to more consumers finally.
- Having a Competitive Edge over Competition:
Businesses that use big data are able to project more superior business models and make better predictions that allow them to have the edge over their competitors who are using more traditional methods. Forecasting is more accurate with big data, and companies can directly increase their performance in the market with the help of these advanced insights.
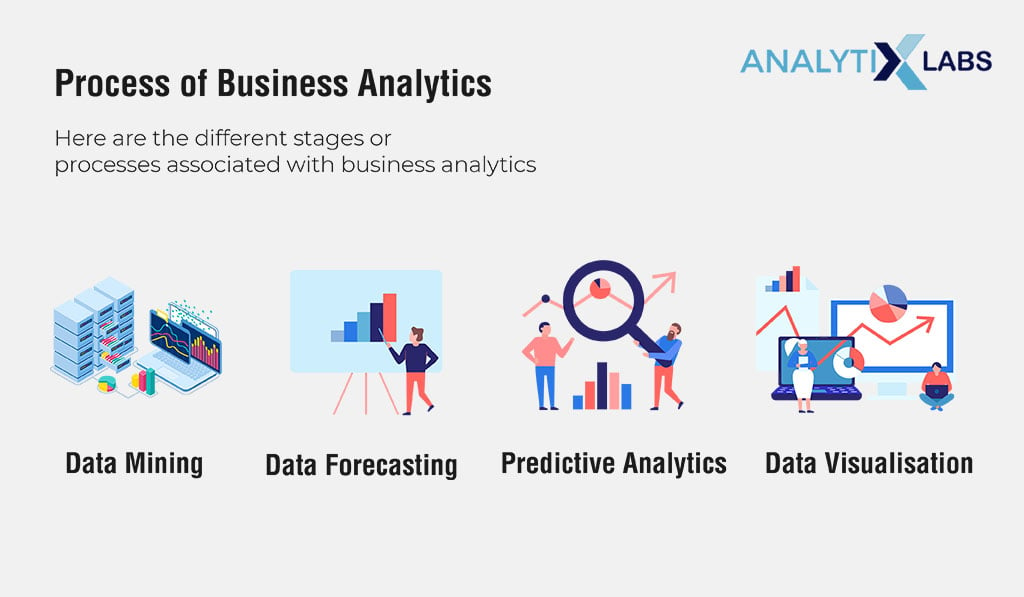
7. Process of Business Analytics
Here are the different stages or processes associated with business analytics:
- Data Mining: Mining data is one of the most important things in business analytics, meaning that without data mining, businesses would not be able to extract cognizable information from structured and especially unstructured data. Data mining is performed with the help of statistical tools or machine learning in order to identify past trends and hidden patterns in data by analysing them. Once the data is processed or mined, it is transferred into data warehouses where it can be shared with multi-dimensional databases. Business analysts are then tasked with examining these patterns and presenting them in charts, plots or graphs.
- Data Forecasting: Forecasting is a very important process that involves deep analytics of past or historical data in order to estimate the performance of products, the condition of the market or customer behaviour. This can also help forecast events that require an allocation of budget. Machine learning is crucial for accurate forecasting. Data forecasting is highly used for forecasting market conditions, financial statuses, asset requirements and other future requirements. For more details, please read Business Forecasting: Meaning, Methods & More
- Predictive Analytics: This is similar to data forecasting, however, this is even more advanced as it uses Artificial Intelligence to evaluate risk and potential abnormalities. This allows businesses to make better decisions. Predictive analytics facilitates informed operational decisions that take aberrations, anomalies or potential events into account. Predictive analytics can also help cut ahead of the competition with the power of data. Predictive analytics help marketers and advertisers recommend products and services to customers more effectively as well.
- Data Visualisation: This is one of the most important processes that represent insights in cognizable formats such as diagrams, tables, graphs and charts. This helps identify patterns in data manually with ease and makes reporting to non-technical staff and stakeholders easier. Visualisation is also important for projecting the important information in data using the best possible (compact but informative) method from massive datasets.
8. Scope And Future of Business Analytics
The scope of business analytics is massive, and the future seems bright for people pursuing this field. More than 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are generated every day, thus ensuring that businesses cannot function without business analytics anymore. The world produces more data now in two days than we did in total from the beginning of civilization till 2003. This simply reinforces the fact that if we wish to effectively use this data to enhance the performance of our website, business, product, service, we must rely on business analytics.
53% of companies use business and data analytics in their daily operations, while many smaller enterprises have started adopting analytics ever since the Covid-19 pandemic started. Business analytics is also one of the most desirable jobs now, with companies always in dire need of skilled analysts. The growing dependency on data and the reliance on business analytics will only increase with more advancements in technology and a more fast-paced world where the competition is armed equally well with business intelligence and data.
You may also like to read: Scope of Business Analytics In India | Business Analytics Future
9. FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the three types of business analytics?
Technically speaking, the three types of business analytics are descriptive analytics, predictive analytics, and prescriptive analytics. However, when talking about job roles, the three most common types of business analytics (other than general business analytics) are financial analytics, marketing analytics, and operations analytics.
You may also like to read in detail: Types of Business Analytics – Types of Analytics With Examples
Q2. What are the elements of business analytics?
The different elements or components of business analytics are data acquisition, data management, data governance, data security, interpretation, identification, insights, prediction, forecasting, data storage, data visualization, and finally, data optimization.
Q3. Who are the users of business analytics?
Individuals and professionals from all fields and industries are users of business analytics. Common users of business analytics would be businessmen, corporate professionals, analysts, bankers, marketers, advertisers, managers, and website owners.
You may also like to read: What Does a Business Analyst Do? Responsibilities, Roles & Salary
10. Conclusion
The importance of data analytics in business is massive; companies cannot operate effectively in this day and age without relying on data and business analytics. Businesses can reduce wastage, remove errors, and increase revenue with business analytics. Ever since data started being used for making business decisions, the world has changed drastically, with products and services getting better and consumers getting exactly what they want, when they want, without much effort.
You may also like to read:
1. Best Ways To Learn Business Analytics | Courses & Free Resources
2. How to Become a Business Analytics Professional? Salary, Skills, Courses
3. Differences Between Business Analytics And Data Analytics | AnalytixLabs








