Data engineers and scientists are ruling the data domain, and why not. Companies, big and small, across all industries and domains, are generating huge amounts of data that needs cleaning and analysis. The debate on data engineer vs. data scientist keeps cropping up every now and then because –
- Both deal with data
- Both have skills and roles overlapping with each other
Yet, they are different. While both deal with data, they have distinct responsibilities and skill sets to be successful.
Data engineers build and maintain infrastructure to store, process, and transport massive volumes of data. Whereas data scientists analyze and interpret data to inform decision-making.
Many critics often question -which one is better.
Overall, the scope for both data science engineers and data scientists is vast. Moreover, opportunities for both of them continue to grow as the need for data-driven insights becomes more critical for businesses across industries.
This article explores the difference between data engineer and data scientist. We will compare data engineer vs data scientist, which is better, and discuss their scope.
Data Engineer vs Data scientist: An Overview
| Data engineering is concerned with the technical workflow of collecting, storing, organizing, processing, and visualizing data.
Theya re primarily concerned with the raw data’s production readiness and components like formats, resilience, scaling, data storage, and security. |
Data scientists focus on meaning from raw data through statistical analysis and machine learning techniques.
They uncover trends in data that can be used by businesses for strategic planning. |
Data engineers are typically well-versed in IT skills such as coding, system design, database management, monitoring, and optimization. They understand mathematics and statistics since they need to apply analytical skills to develop algorithms that process large volumes of structured or unstructured data.
Planning, constructing, testing, integrating, managing, and optimizing data from various sources is part of their key responsibilities.
Data engineers have excellent communication skills and an understanding of business objectives to develop data solutions that meet decision-makers’ needs. They can write complex queries in Structured Query Language (SQL) for extracting, transforming, and integrating data into applications.
Read: What is Data Engineering – roles, responsibilities, and skills
Data scientists use programming languages such as Python, R, and SAS to explore large datasets, perform statistical analysis and build machine learning models. They also develop algorithms to automate data collection, cleaning, and transformation processes.
They interact with corporate executives to comprehend their demands and deliver complex findings for business decision-makers.
Data scientists have strong problem-solving skills that help extract information from raw data. Additionally, they are well-versed and can communicate their findings clearly and concisely to stakeholders within the organization.
Data Process: The Hierarchy
While there are instances where the roles of a data science engineer and a data scientist overlap, there is still difference between data engineer and data scientist when it comes to the data demands.
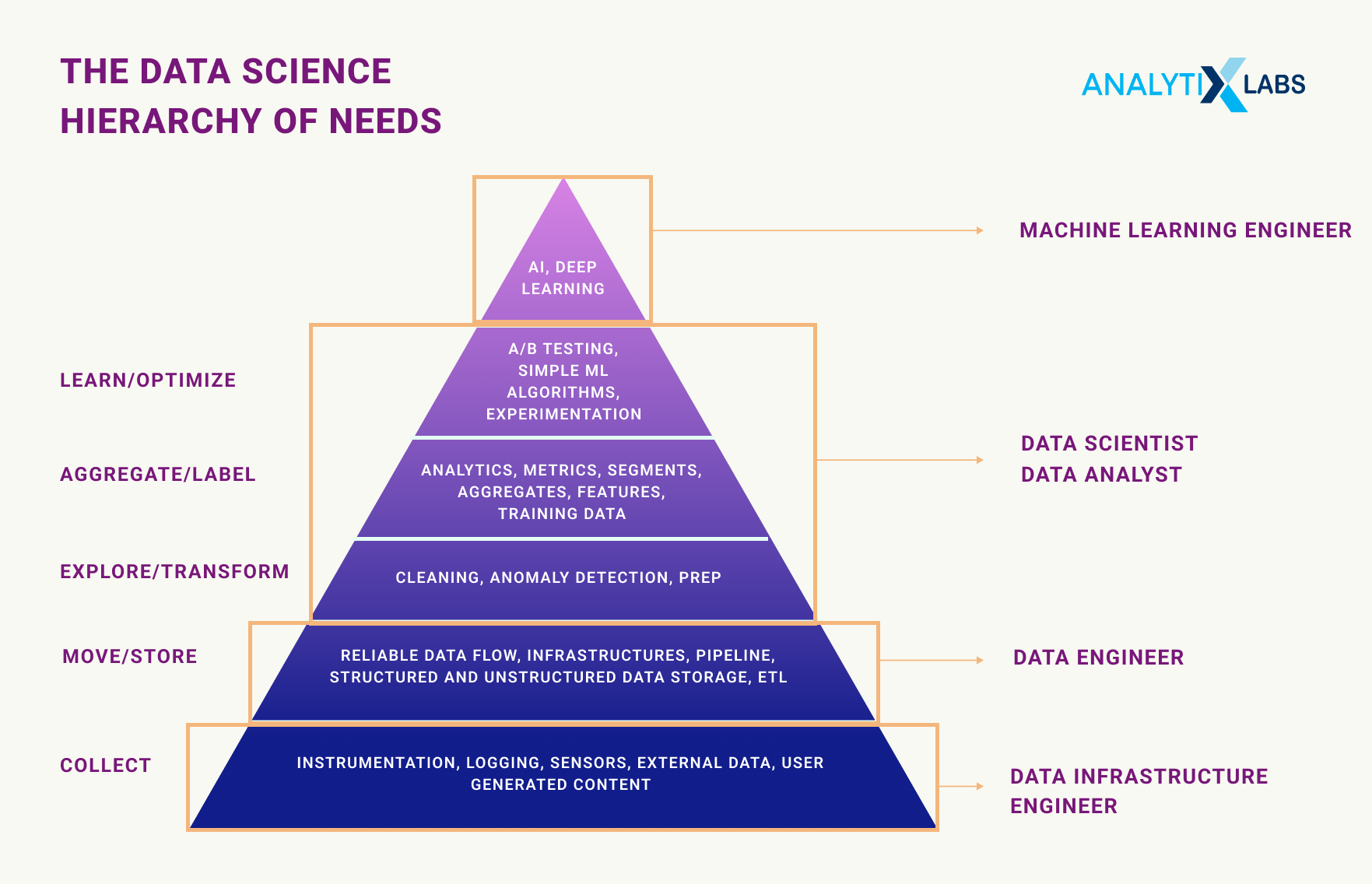
Projects involving data typically have a timeline. They begin with an aim, which is frequently characterized as a challenge. The data project’s goal is to use data to address that issue.
The issue might be commercial or not.
Data engineering and data science typically occur at different points on the project’s timeline and hierarchy of demands once the problem has been identified.
The tasks at the base of the pyramid are a task’s absolute prerequisites , according to the data science hierarchy of needs.
Tier 1: Collect data – Data engineering
The base of this pyramid is where data engineering services are primarily provided. The data science engineer is completely within their purview regarding instrumentation, logging, sensors, external data, and user-generated material.
Tier 2: Move/store data – Data engineering
The data science engineer is still responsible for infrastructure, pipelines, ETL, and data storage. They shift the raw data and suggest using it throughout the timeline.
Tier 3: Explore/transform data – [both] Data science & Data engineer
Again, much of this is done during data engineering, but cleaning and anomaly detection are typically collaborative efforts. This step frequently includes adding data to dashboards for analysis.
Tier 4: Aggregate/label data – Data science
The software has loaded the data for exploration at tier four of the pyramid. It has been revealed, found, and is now subject to evaluation. It now falls under the control of the data scientist. The creation of hypotheses and preliminary analyses takes place.
Tier 5: Learn/optimize data – Data science & ML engineer
A trained data scientist or machine learning engineer may or may not be responsible for model construction. The findings of testing hypotheses are refined. Data may be used to train machine learning (ML) algorithms that perform deep learning, or it may be utilized to develop artificial intelligence (AI) implemented in hardware and/or software platforms.
Read: Data Scientist vs Machine Learning Engineer: What is the difference?
Role Differences: Data Scientist vs. Data Engineers
What does a data engineer do?
Data engineers are responsible for developing the tools, architectures, and systems that enable data collection.
These are the means of gathering data, allowing the obtained data to be divided, assessed, or analyzed. Data scientists would struggle to perform their duties without them. They frequently work with data sets to find trends or patterns, which might help them when developing algorithms to understand raw data.
Here are some other responsibilities of a data engineer:
- Data programming language should be used and translated.
- Data organization and preparation for predictive and prescriptive modeling.
- Align the system design with the needs or demands of the client.
- Actively seek ways to improve data reliability, effectiveness, and quality.
- Use statistical and machine learning techniques to improve consumer or corporate operations.
What does a data scientist do?
While data engineers create the technologies that collect data, data scientists analyze the data sets.
Data scientists use their years of knowledge to interpret data sets, which may involve objectively evaluating the data or formulating hypotheses based on what the data indicates. These initiatives may use predictive modeling, sophisticated analytics, and machine learning thanks to the framework made available by data engineers.
Data scientists additionally perform the following tasks:
- In order to analyze data more effectively, develop or improve statistical learning models.
- Contribute to the procedures of predictive modeling.
- Consult other engineers, such as software developers, mechanical experts, or computer scientists.
- Share findings with project stakeholders.
- Verify and corroborate the data to ensure data correctness and uniformity.
- Large data set repositories to mine.
- To improve data reliability, clean and validate it.
Learning Path: Data Scientist vs. Data Engineer
-
Data Engineer
Data engineers usually come from the software engineering domain and are skilled in languages like Java, Python, SQL, and Scala. Alternatively, they might hold a degree in statistics or mathematics, enabling them to use various mathematical techniques to address business issues.
Most employers prefer recruiting data engineers with bachelor’s degrees in computer science, applied mathematics, or information technology.
Candidates might also need a few certifications in data engineering, such as Google’s Professional Data Engineer or AnalytixLab’s Certified Data Engineering Course. It also helps if they have expertise in creating big data warehouses that can perform some Extract, Transform, and Load, or ETL, on Big Data.
-
Data Scientist
A college degree in computer science, data science, or a related subject is typically required to become a data scientist. Additionally, many data scientists enroll in graduate programs, expert certifications, and boot camps.
A strong computer science and mathematics foundation is normally required when becoming a data scientist, as is previous experience working with significant amounts of data. Additionally, knowing statistical analysis and machine learning is often beneficial.
Data scientists must be familiar with tools like Hive, Hadoop, Cassandra, and MongoDB and computer languages like SQL, Python, R, and Java.
Learning Path:
Data Scientist vs Data Engineer Salary
The data scientist vs data engineer salary typically depends on their experience, job role, and the industry. Below is a comparative study on the salary difference across industries, cities, and by experience [in India].
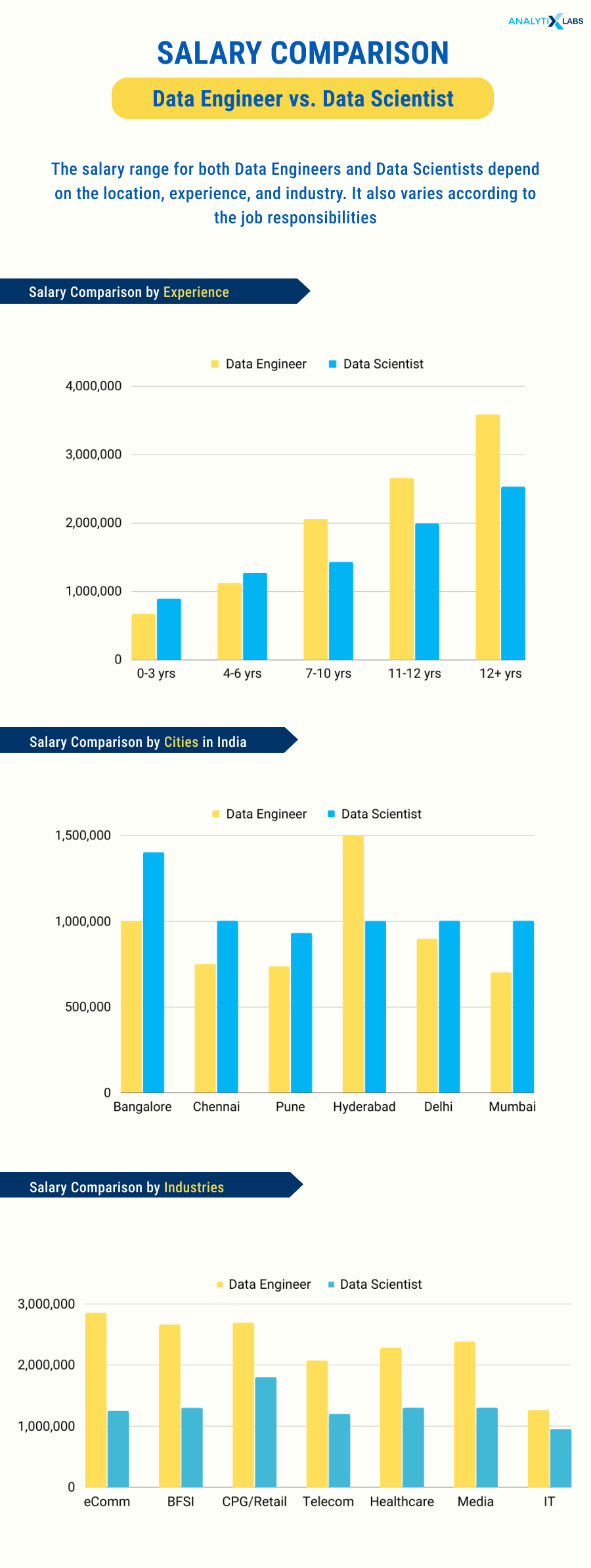
Key findings:
- Data engineers are typically well-paid compared to many other jobs. However, actual salaries can vary significantly depending on the specific industry, the organization’s size, and the data engineer’s experience level.
- Bangalore has the highest salary bracket for both roles since it is the tech hub of India; quickly followed by Delhi, which is witnessing a huge leap in the data market.
- eCommerce domain has the maximum salary for data professionals because this industry has the maximum data in terms of transactions, user behavior, browsing, etc., and is closely followed by Banking and Finance sector.
Career Path: Which is better?
Data Scientist is an entry-level position while Data Engineering is for more seasoned data professionals.
A data professional follows the below career path:
Data Scientist > Data Analyst > Data Engineers > Business Intelligence Developer
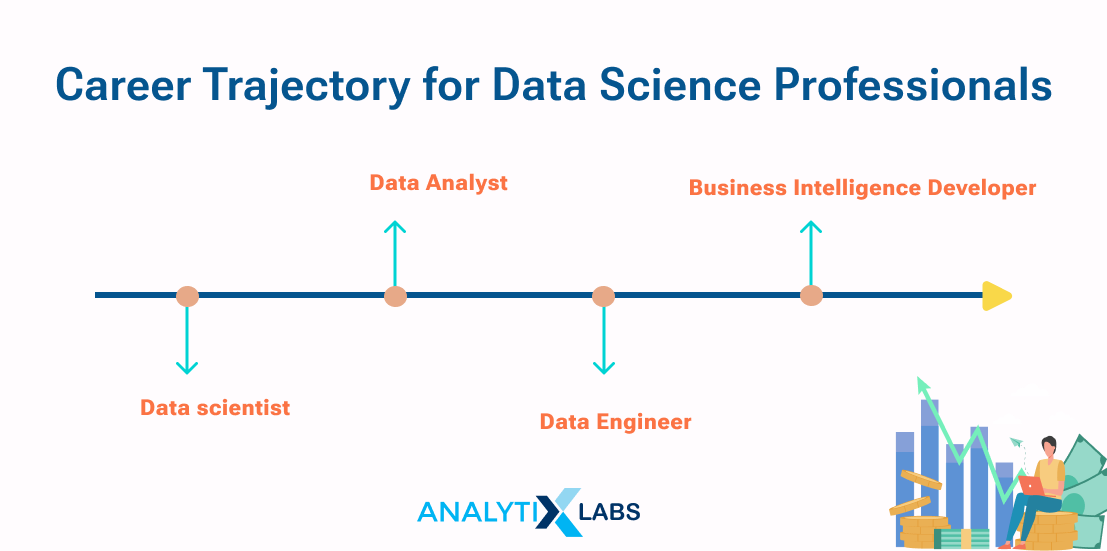
Data scientists begin their careers in entry-level data science positions through an internship or as junior data scientists. Before moving on to creating their experiments and tackling more difficult business issues, these entry-level positions give new data scientists a chance to continue honing their technical skills.
With experience, data science professionals proceed to more complex and challenging roles while narrowing their expertise.
Many data engineers use positions like data architect, solutions architect, and database developer to enhance their data engineering skills, obtain more information about data processing, learn cloud computing, and acquire experience with ETL and data layers.
Before moving into data engineering, some also use data analytics to advance their understanding of what data analysts and scientists require.
-
Who should become a data scientist?
Data scientists are analytical thinkers who are curious. They do not mind putting in queries and are keen to test their hypotheses. Data scientists use data to analyze past events, spot trends, and predict what may happen soon.
If you appreciate developing machine learning algorithms, performing complex statistical analysis, and finding innovative solutions to problems, a career as a data scientist may be ideal for you.
The ideal candidate for a data science role is someone with strong analytical skills who is comfortable working with large amounts of data. You must also have excellent problem-solving abilities and effectively communicate your findings to colleagues and other stakeholders.
-
Who should become a data engineer?
Data engineers are primarily interested in the architecture and infrastructure used to store and organize data. They are strong developers who appreciate learning and using the most recent technologies, discovering new techniques to improve software and processes, and thriving on time and resource savings for a firm.
If you enjoy experimenting with new tools and technologies and are constantly looking for ways to improve the products you create, data engineering may be the right career path for you.
Skills: Data Engineer vs Data Scientist
Data engineers are responsible for building and maintaining systems that collect, store, process, and analyze data. To be successful in this role, they must have a combination of technical expertise and business acumen.
Data scientists should have soft skills, such as the ability to communicate effectively with stakeholders and other professionals from different disciplines. It includes being able to translate complex data into visualizations or actionable insights in a way that non-technical audiences can understand.
| Data Engineer | Data Scientist |
|
|
Conclusion
The role of data engineer and data scientist has the potential to continue its upward trajectory in the coming years. With evolving technology, companies increasingly rely on big data analytics to make important decisions.
As a result, data engineers will be needed to create reliable pipelines for storing and analyzing large amounts of data. In contrast, data scientists can help companies uncover valuable insights from that data.
It could mean an even greater demand for professionals with these skill sets in the future as organizations look for in-depth analysis and sophisticated solutions.
Furthermore, a combination of both data engineering and data science roles is becoming increasingly popular as businesses seek knowledgeable personnel.
They prefer those who possess both technical engineering knowledge and advanced analytical capabilities.

![Data Engineer vs. Data Scientist – A Comparative Study [Jobs, Salary, and Skills] data engineer vs data scientist](https://www.analytixlabs.co.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/data-engineer-vs-data-scientist-770x515.png)



![Tree Traversal in Data Structure Using Python [with Codes] tree traversal in data structure](https://www.analytixlabs.co.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Cover-Image-1-370x245.jpg)


